WHAT IS FOLLICULITIS?
Folliculitis means an inflammation or infection of the hair follicles of the skin. Most of the skin is covered with tiny hairs which grow out of hair follicles. In folliculitis, many hair follicles in one area of the skin are affected.
Folliculitis typically occurs in areas of irritation, such as sites of shaving, skin friction, or rubbing from clothes. In most cases of folliculitis, the inflamed follicles are infected with bacteria, especially with Staphylococcus organisms, that normally live on the skin.
The most common factors that contribute to the development of folliculitis include:
- Irritation from shaving;
- Friction from tight clothing;
- A pre-existing skin condition, such as eczema, acne, or another dermatitis (inflammation of the skin);
- Injuries to the skin, such as abrasions;
- Extended contact from plastic bandages or adhesive tape.

WHY DOES FOLLICULITIS OCCUR?
Most cases of folliculitis are due to an infection with a germ (bacterium) called Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus). This bacterium is carried harmlessly in the noses of many people, without causing any problems. Occasionally, other germs (bacteria) are the cause of folliculitis.
Folliculitis usually occurs at sites where hair follicles are damaged by friction or shaving, or where there is blockage of the follicle. Excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis) due to overactivity of the sweat glands can be another cause. Sometimes, using a steroid cream on the face can trigger a bout of folliculitis. The most common site affected is the beard area of men although women with facial hair can get it in this area too. Other common sites for folliculitis are the arms, legs, armpits and buttocks.
RISK FACTORS
Risk factors for folliculitis include:
- Diabetes;
- Suppressed immune system due to HIV, organ transplantation, or cancer;
- An underlying skin condition, such as eczema, acne, or another dermatitis;
- Obesity;
- Frequent shaving;
- Pressure (prolonged sitting on the buttocks).
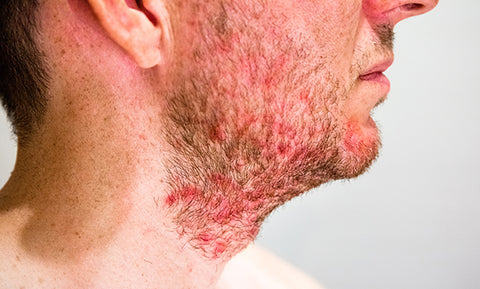
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
The most common locations for folliculitis include:
- Scalp
- Beard area in men
- Underarms, groin, or legs in women
- Buttocks
- Thighs
Individual lesions of folliculitis include pus-filled bumps (pustules) centered on hair follicles. These pus-filled bumps may be pierced by an ingrown hair, can vary in size from 2–5 mm, and are often surrounded by a rim of pink to red, inflamed skin. Occasionally, a folliculitis lesion can erupt to form a scab on the surface of the skin.
Mild and moderate cases of folliculitis are often tender or itchy. More severe cases of folliculitis, which may be deeper and may affect the entire hair follicle, may be painful.
Mild and moderate cases of folliculitis usually clear quickly with treatment and leave no scars. However, more severe cases of folliculitis may lead to complications, such as cellulitis (an infection of the deeper skin tissue), scarring, or permanent hair loss.
HOW TO PREVENT FOLLICULITIS
Keeping your skin clean, dry and free from abrasions or irritations can help to prevent folliculitis. Certain people are more prone to infections, such as people with diabetes. If you have a medical problem that makes you more likely to get infections, these precautions may be more important. Using antiseptic washes routinely is not generally recommended, as they can make the skin sore and dry. Keeping the skin moisturised can help protect it from damage. Take care when shaving (especially if you wet shave), using a shaving gel, foam or soap to lubricate the blades across the skin to prevent nicks and cuts.
Most cases of folliculitis are not contagious but if you have been identified as carrying the S. aureus germ (bacterium), this infection can occasionally be transferred to other people. This risk can be minimised by normal hygiene measures and laundering clothing, bed linens and towels on a hot wash. Do not share razors. You should also avoid sharing hot tubs until the infection has been treated.

HOW TO TREAT FOLLICULITIS
Wherever the folliculitis occurs, the treatment principle is broadly the same. General measures involve avoiding things that aggravate the condition. It is important to shave in the direction of hair growth. Sometimes it is worth taking a break from shaving for a few days, to let the folliculitis settle down by itself. Tight clothing over the affected area, particularly if it makes you sweat, will not help either. Keeping cool and keeping folliculitis exposed to the fresh air will also help. If you have folliculitis you should not share towels, flannels or razors.
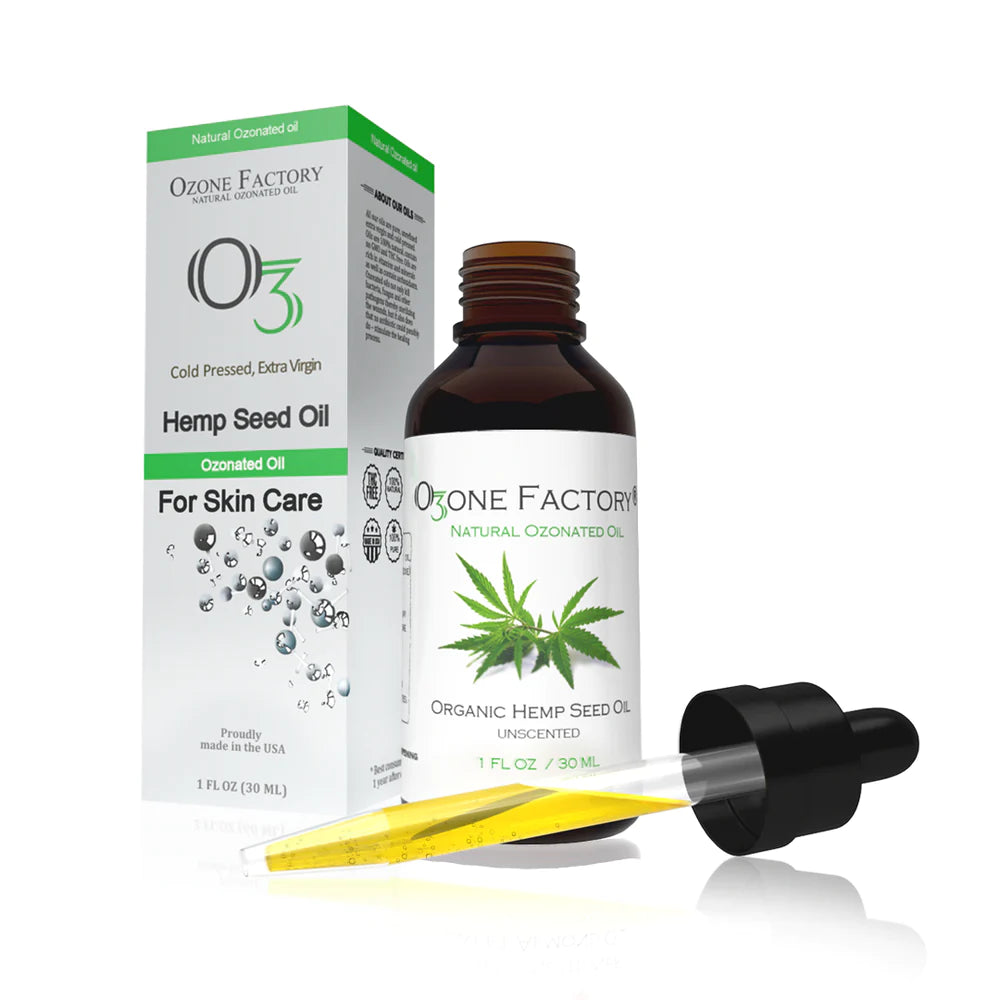
CAN YOU USE OZONATED OIL FOR FOLLICULITIS?
The therapeutic and health properties of oils such as coconut oil and grapeseed oil, have been known for millennia. However, it has been demonstrated that it is possible to further enhance the properties of oils by adding ozone. Indeed, ozone (O3) has been recognized as one of the best bactericidal, antiviral, and antifungal agents, and has been used empirically as a clinical therapeutic agent.
Coconut ozonated oil - Research shows that daily use of ozonated coconut oil on the infected area can reduce irritation and inflammation. This needs to be applied once daily for better results. Ozonated coconut oil contains fats, which are not only good for consumption in the dishes but also good for the skin. These fatty acids are absorbed by the skin and help in a speedy recovery.
Grapeseed ozonated oil - When used as a topical treatment, grapeseed ozonated oil can help promote healthy skin on a cellular level. That’s because grapeseed oil contains vitamin E, beta-carotene, and linoleic acid. These nutrients give the oil antioxidant and antiproliferative properties, helping healthy cells to regenerate and replace aging or damaged cells. Natural oils that contain high levels of certain fatty acids — like grapeseed — have also been linked to wound healing. Grapeseed ozonated oil has antimicrobial properties, which means it can kill bacteria. While there are no large scale studies proving a link between grapeseed oil and folliculitis treatment, it may be worth a try.






